
What are the Materials and Standards of Spiral Pipes?
Spiral pipe & tube (SSAW Pipe) is a form of pipe, which is made of thin plates that are continuously rolled. Due to its unique structure, spiral pipes are widely used in many fields, such as petroleum, natural gas, chemical industry, shipbuilding, water conservancy and other engineering fields, as well as structural engineering fields such as construction and bridges.
Common spiral pipe materials:
Spiral pipes are made of a wide variety of materials, and commonly used materials include carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, etc. The commonly used spiral pipe materials and their characteristics are introduced below.
1. Carbon steel spiral pipe
Carbon steel spiral pipes are widely used in construction, shipbuilding, water conservancy and other fields. Its main features are low price, high strength and good toughness, and it can be applied to various environments. However, carbon steel spiral pipes have poor corrosion resistance and cannot be suitable for working environments with special requirements.

2. Stainless steel spiral pipe
Stainless steel spiral pipes are suitable for working environments that require strong corrosion resistance, such as food, medicine, chemical industry and other fields. Stainless steel spiral pipe has excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, good toughness, high temperature resistance, impact resistance and other characteristics. However, stainless steel spiral pipes are more expensive, require strict manufacturing processes, and need to choose appropriate methods during processing and welding.
3. Alloy steel spiral pipe
Alloy steel spiral pipe is mainly composed of molybdenum, chromium, cobalt, nickel and other elements, and has the characteristics of strong corrosion resistance, high strength and high hardness. Alloy steel spiral pipes have a wide range of applications and are mainly used in harsh working environments such as petroleum, natural gas, and chemical industries. However, alloy steel spiral pipes have high manufacturing process requirements, high costs, and difficult processing.
Carbon steel spiral pipe implementation standards:
1. ASTM standard
The ASTM standard is a standard issued by the American Society for Testing and Materials that regulates the production of carbon steel spiral welded steel pipes. ASTM standards stipulate the chemical composition, mechanical properties, dimensions, allowable cracks, defect levels and other indicators of pipes. Its representative standards include ASTM A53/A53M, ASTM A252, etc.
2. API standard
The API standard is a standard issued by the American Petroleum Institute. It is mainly used in the production and manufacturing of oil and gas transportation, downhole oil production and drilling equipment. It also has regulations on the production of carbon steel spiral pipes. API standards include two parts: API SPEC 5L and API SPEC 5CT. API SPEC 5L is used for oil and gas transmission pipelines, and API SPEC 5CT is used for the manufacturing of oil well casing.
3. DIN standard
The DIN standard is a standard formulated by the German national standards agency. The DIN standard also has corresponding specifications for the production of carbon steel spiral pipes. DIN standards mainly include DIN 2458, DIN 17175 and DIN EN 10217-1, among which DIN 2458 is suitable for steel pipes transporting fluids under non-pressure, DIN 17175 is suitable for boilers and pipes under high temperature and high pressure, and DIN EN 10217-1 is suitable for pressure Steel pipes in the system.
4. GB standard
GB standard refers to China's national standard. The implementation standards of spiral welded pipe include: GB/T9711-2017; GB/T3091-2015; SY/T5037-2018. Among these three standards, there are relevant technical requirements and specifications for the production, manufacturing, inspection, chemical composition, mechanical properties, hydraulic testing, and non-destructive testing of spiral welded pipes.
Among them, the GB/T9711 standard is a national standard, mainly for steel pipes used in oil and gas industry pipelines, including seamless steel pipes and welded steel pipes, and is more stringent than the other two standards. Among them are GB/T9711.1 (representing Grade A steel) and GB/T9711.2 (representing Grade B steel). The quality and test requirements included in GB9711.2 are generally higher than those of GB9711.1. GB9711.2 Generally applicable to steel pipes for transporting flammable fluids, not cast pipes.
The GB/T3091 standard is also a national standard and is a standard for steel pipes for low-pressure fluid transportation, which means welded steel pipes for transporting fluids with lower pressures. Welded steel pipes include spiral welded pipes and straight seam welded pipes.
The SY/T5037 standard is a ministry standard, mainly used for submerged arc welded steel pipes for water supply and drainage of low-pressure fluids. Submerged arc welded steel pipes include spiral submerged arc welded steel pipes (spiral welded pipes) and straight seam submerged arc welded steel pipes.
The SY/T5037 standard is a standard with lower requirements. The standard stipulates the materials used for spiral welded pipes and hydraulic pressure testing. However, X-ray non-destructive testing only requires 20% spot inspection, while the other two national standards It is 100% X-ray inspection.
When spiral welded pipes are used in different engineering situations, different standards will be required. Production, manufacturing, testing, and delivery must all be implemented in accordance with the standards. There is no circle without rules. There must be a standard for judging the quality of spiral welded pipes, and with the implementation standards of spiral steel pipes, there is a basis for judgment. Spiral welded pipe manufacturers produce, inspect, and deliver products in accordance with the standards given by users, which is more conducive to market fairness.
The main materials are: Q195, Q215, Q235, Q255 and Q275, etc. Among them, Q195, Q215, and Q235 are relatively commonly used materials, with good toughness and plasticity, and are suitable for low-pressure fluid transportation and construction. Q255 and Q275 are relatively high-strength materials, with high strength and stiffness, and are suitable for In fields such as high-pressure fluid transportation and construction.
Standard difference analysis:
Although ASTM, API, DIN, and GB standards all regulate the production of carbon steel spiral pipes, these standards have certain differences in the production process, chemical composition, mechanical properties, dimensions, etc. of the pipes. Usually, users need to choose appropriate standards and specifications based on specific usage scenarios. For example, in oil and gas transmission pipelines, pipes with higher strength and corrosion resistance are required. In this case, API SPEC 5L standard pipes can be selected. In general water supply and drainage projects, ASTM A53/A53M standard pipes are enough to meet the needs.
Production process of carbon steel spiral steel pipe (SSAW):
Carbon steel spiral steel pipe is made by rolling low-carbon carbon structural steel into a pipe blank at a certain spiral angle, and then welding the pipe seams. It can produce large-diameter steel pipes from narrower strips of steel.
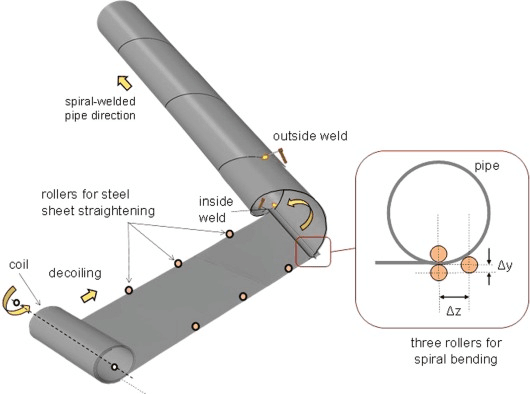
(1) Raw materials are strip steel coils, welding wires, and fluxes. Before putting into use, they must go through strict physical and chemical tests.
(2) The head-to-tail butt joint of strip steel adopts single-wire or double-wire submerged arc welding, and automatic submerged arc welding is used for repair welding after being rolled into steel pipes.
(3) Before forming, the strip steel is leveled, trimmed, planed, surface cleaned, transported and pre-bent.
(4) Electric contact pressure gauges are used to control the pressure of the cylinders on both sides of the conveyor to ensure the smooth conveying of the strip.
(5) Adopt external control or internal control roll forming.
(6) The weld gap control device is used to ensure that the weld gap meets the welding requirements, and the pipe diameter, misalignment and weld gap are strictly controlled.
(7) Both internal welding and external welding use American Lincoln welding machine for single-wire or double-wire submerged arc welding, so as to obtain stable welding quality.
(8) All the welded seams are inspected by the online continuous ultrasonic automatic flaw detector, which ensures 100% non-destructive testing coverage of the spiral welds. If there is a defect, it will automatically alarm and spray the mark, and the production workers can adjust the process parameters at any time according to this to eliminate the defect in time.
(9) Use an air plasma cutting machine to cut the steel pipe into single pieces.
(10) After cutting into single steel pipes, each batch of steel pipes must undergo a strict first inspection system to check the mechanical properties, chemical composition, fusion status of the welds, steel pipe surface quality and non-destructive testing to ensure that the pipe making process is qualified before it can be formally put into production.
(11) The parts marked by continuous ultrasonic flaw detection on the weld shall undergo manual ultrasonic and X-ray re-examination. If there are indeed defects, after repairing, they shall undergo non-destructive inspection again until the defects are confirmed to be eliminated.
(12) The tubes where the strip steel butt welds and the D-joints intersected with the spiral welds are all inspected by X-ray TV or film.
(13) Each steel pipe has undergone a hydrostatic pressure test, and the pressure is radially sealed. The test pressure and time are strictly controlled by the steel pipe water pressure microcomputer detection device. The test parameters are automatically printed and recorded.
(14) The pipe end is machined to accurately control the verticality of the end face, the bevel angle and the blunt edge.
The main process characteristics of spiral steel pipe:
a. During the forming process, the deformation of the steel plate is uniform, the residual stress is small, and the surface does not produce scratches. The processed spiral steel pipe has greater flexibility in the size and specification range of diameter and wall thickness, especially in the production of high-grade thick-walled pipes, especially small and medium-diameter thick-walled pipes.
b. Using advanced double-sided submerged arc welding technology, welding can be realized at the best position, and it is not easy to have defects such as misalignment, welding deviation and incomplete penetration, and it is easy to control the welding quality.
c. Carry out 100% quality inspection of steel pipes, so that the whole process of steel pipe production is under effective inspection and monitoring, effectively ensuring product quality.
d. All the equipment of the entire production line has the function of networking with the computer data acquisition system to realize real-time data transmission, and the technical parameters in the production process are checked by the central control room.
The stacking principles of spiral steel pipes require:
1. The principle requirement of spiral steel pipe stacking is to stack according to varieties and specifications under the premise of stable stacking and ensuring safety. Different types of materials should be stacked separately to prevent confusion and mutual erosion;
2. It is forbidden to store items that corrode steel around the stack of spiral steel pipes;
3. The bottom of the spiral steel pipe pile should be high, firm and flat to prevent the material from being damp or deformed;
4. The same material is stacked separately according to the order of storage;
5. For the spiral steel pipe sections stacked in the open air, there must be wooden pads or stone strips underneath, and the stacking surface is slightly inclined to facilitate drainage, and attention should be paid to placing the materials straight to prevent bending deformation;
6. The stacking height of spiral steel pipes shall not exceed 1.2m for manual work, 1.5m for mechanical work, and the stack width shall not exceed 2.5m;
7. There should be a certain channel between the stacks. The inspection channel is generally 0.5m, and the access channel depends on the size of the material and the transport machinery, generally 1.5-2.0m;
8. The angle steel and channel steel should be stacked in the open air, that is, the mouth should face downward, and the I-beam should be placed vertically. The I-channel surface of the steel should not face upward, so as to avoid water accumulation and rust;
9. The bottom of the stack is raised. If the warehouse is on a sunny concrete floor, it can be raised by 0.1m; if it is a mud floor, it must be raised by 0.2-0.5m. If it is an open field, the concrete floor shall be cushioned with a height of 0.3-0.5m, and the sand and mud surface shall be cushioned with a height of 0.5-0.7m.
Summarize:
As a widely used form of pipe, spiral pipe material selection has an important impact on work in different fields and environments. Carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel are all commonly used materials for spiral pipes, and each has its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of scope of application, characteristics, and price. In practical applications, appropriate materials should be selected accordingly to achieve the best cost performance and use effect.


