
Seamless Steel Pipe Manufacturing Process
The production method of seamless steel pipe (SMLS) is roughly divided into a cross-rolling method (Mengnesmann method) and an extrusion method. The cross-rolling method (Mennesmann method) is to first pierce the tube with a diagonal roll and then extend it with a rolling mill. This method has a high production speed, but has high requirements on the processability of the tube blank, and is mainly suitable for the production of carbon steel and low alloy steel tubes. The extrusion method uses a piercing machine to perforate a tube blank or a steel ingot, and then extrudes it into a steel tube by an extruder. This method is less efficient than the cross-rolling method and is suitable for producing a high-strength alloy steel tube.

Both the cross-rolling method and the extrusion method must first heat the tube blank or the ingot, and the produced steel tube is called a hot rolled tube. Steel pipes produced by hot working can sometimes be cold worked as needed. There are two methods for cold working: one is cold drawing, which is to pull the steel pipe through the extruding die to make the steel pipe become thinner and longer; the other method is cold rolling, which is invented by the Mengnesmann brothers. The hot rolling mill is applied to the method in cold working. The cold working of seamless steel tubes can improve the dimensional accuracy and processing finish of steel pipes and improve the mechanical properties of materials.
Production process of seamless steel pipe (hot rolled steel pipe): The seamlessness of steel pipe is mainly achieved by tension reduction. The tension reduction process is a continuous rolling process of hollow base metal without core rod. Under the condition of ensuring the quality of the welding of the parent pipe, the pipe tension reduction process is to heat the whole welded pipe to 950 degrees Celsius or more, and then to various outer diameters and walls by a tension reducer (a total of 24 times of the tension reducer). Thick finished tube.
The hot-rolled steel pipe produced by this process is intrinsically different from the ordinary high-frequency welded pipe. After heating by the heating furnace, the metallographic structure and mechanical properties of the weld bead and the parent body can be completely consistent. In addition, the multi-pass tension reduction is achieved. Machine rolling and automatic control make the dimensional accuracy of the steel pipe (especially the roundness and wall thickness accuracy of the pipe) superior to similar seamless pipes. In the fluid pipes produced by developed countries in the world, the seamless process of welded pipes has been widely used in boiler tubes. With the development of society, the situation that domestic hot-rolled welded pipes gradually replace seamless pipes has been formed.
Seamless steel pipe manufacturing process:
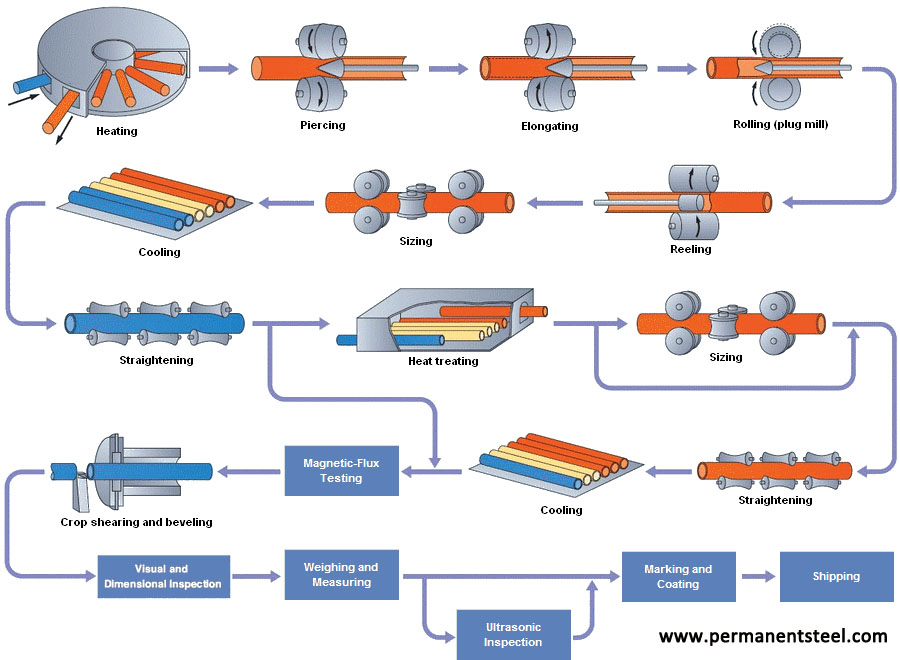
①Main production process of hot-rolled seamless steel pipe (△main inspection process):
Tube blank preparation and inspection △→Tube heating→Perforation→Rolling pipe→Steel pipe reheating→fixed (reduced) diameter→Heat treatment△→Finish pipe straightening→Finishing→Inspection△(non-destructive, physical and chemical, bench inspection)
②Main production process of cold-rolled (drawn) seamless steel pipe:
Blank preparation → pickling and lubrication → cold rolling (drawing) → heat treatment → straightening → finishing → inspection
Go here to learn more about " Introduction and Advantages of Galvanizing Process "
- 【Prev】 : Seamless Steel Pipe
- 【Next】 : Several Production Methods for Seamless Tubes


